Problem 1.
K[Al(OH)4] + H2S = KHS + Al(OH)3 + H2O.
Problem 2.
1) 3Ca + 2P = Ca3P2 (P-3);
2) Ca3P2 + 6HCl = 3CaCl2 + 2PH3 ![]() (P-3);
(P-3);
3) PH3 + 2O2 = H3PO4 (P+5);
4) H3PO4 + NaOH = NaH2PO4 (P+5) + H2O.
Problem 3.
1) 2CrBr3 + 3H2O2 + 3H2SO4 = Cr2(SO4)3 + 3Br2 + 6H2O,
2) 2CrBr3 + 3H2O2 + 10KOH = 2K2CrO4 + 6KBr + 8H2O.
Problem 4.
C6H5-CH=CH-CH2CH3 ![]() CH3CH2COOH
CH3CH2COOH ![]() CH3CH2C(O)Cl
CH3CH2C(O)Cl ![]()
![]() CH3CH2COOCH2C6H5.
CH3CH2COOCH2C6H5.
Reactions:
1) 5C6H5-CH=CH-CH2CH3 + 8KMnO4 + 12H2SO4 = 5C6H5COOH + 5CH3CH2COOH + 4K2SO4 + 8MnSO4 + 12H2O.
2) CH3CH2COOH + PCl5 ![]() CH3CH2C(O)Cl + POCl3 + HCl.
CH3CH2C(O)Cl + POCl3 + HCl.
3) CH3CH2C(O)Cl + C6H5CH2OH ![]() CH3CH2COOCH2C6H5 + HCl.
CH3CH2COOCH2C6H5 + HCl.
Problem 5.
Possible solution: A - CH2Cl- CH2Cl, B - C2H2, C - CH3CHO, D - C2H5OH, E - HOCH2CH2OH, F - C2H4, G - H2O.
1) CH2Cl-
CH2Cl + 2KOH(alc. soln.) ![]() C2H2 + 2KCl + 2H2O.
C2H2 + 2KCl + 2H2O.
2) C2H2 + H2O ![]() CH3CHO.
CH3CHO.
3) CH3CHO + H2 ![]() C2H5OH.
C2H5OH.
4) CH2Cl-
CH2Cl + 2KOH(aq. soln.) ![]() HOCH2CH2OH + 2KCl.
HOCH2CH2OH + 2KCl.
5) CH2Cl-
CH2Cl + Mg ![]() C2H4 + MgCl2.
C2H4 + MgCl2.
6) 3C2H4 + 2KMnO4 + 4H2O = 3C2H4(OH)2 + 2MnO2 + 2KOH.
7) C2H4 + H2O ![]() C2H5OH.
C2H5OH.
Problem 6.
|
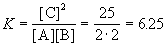
|
In the second case:
|
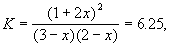
|
![]() (A) = (3-1.115) / 6 = 0.314;
(A) = (3-1.115) / 6 = 0.314;
![]() (B) = (2-1.115) / 6 = 0.148;
(B) = (2-1.115) / 6 = 0.148;
![]() (C) = 0.538.
(C) = 0.538.
Problem 7.
CxHyNz + O2 ![]() xCO2 + y/2 H2O + z/2 N2
xCO2 + y/2 H2O + z/2 N2
1) x : y/2 : z/2 = (30.8/44) : (8.1/18) : (1.4/28) = 7 : 4.5 : 0.5. The empirical formula is C7H9N.
2) The molar mass is: M = mRT / PV = 3.21 . 8.31 . 500 / (99.7 . 1.25) = 107 g/mol. The empirical formula is the true one.
3) Hydrogen addition. 10.7 / 107 = 0.1 mole of substance adds (138.5. 9.0/ /8.31. 500) = 0.3 mole of hydrogen. It means that the substance contains aromatic systems and, hence, belongs to aromatic series of benzene or pyridine. The possible structures:
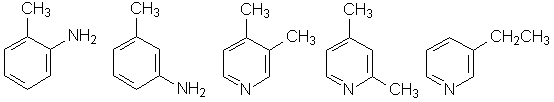
See also:
Chemistry Department of Moscow State University