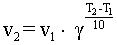Influence of temperature on the velocity of chemical reaction.
The velocities of the most chemical reactions increases with the rise of temperature.
The temperature affects the number and the energy of collisions. The influence of the
temperature on the number of molecule collisions could be shown by the model.
In a first approximation the influence of temperature on the velocity of reactions
is defined by the rule of Vant-Hoff (it was stated by J.H.Vant-Hoff,
who discovered it by analysing a great number of reactions):
|
In a temperature range from 0oC up to 100oC a
10-degree rise of temperature leads to 2-4 time increase of the velocity of chemical reaction
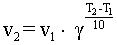
|
where g - the temperature coefficient varying from 2 to 4.
Do you want to know why the rule of Vant-Hoff is
only the first approximation?
The explanation to this rule was given by S. Arrhenius, who stated that just the
strongest collisions between the molecules of reagents lead to reaction. Only the
molecules with an excess of kinetic energy are capable to provoke chemical reaction.
S.Arrhenius calculated the part of active (i.e. bringing to reaction)
impacts of the reacting particles - a, which depends on temperature: a = exp(-E/RT).
From this, he deduced the equation of Arrhenius:
k = koe-E/RT
where ko and E depend on the character of reagents. E is the energy which is necessary
for the molecules to interact, referred to as the energy of activation.
Do you want to know, why?
Supplementary
|